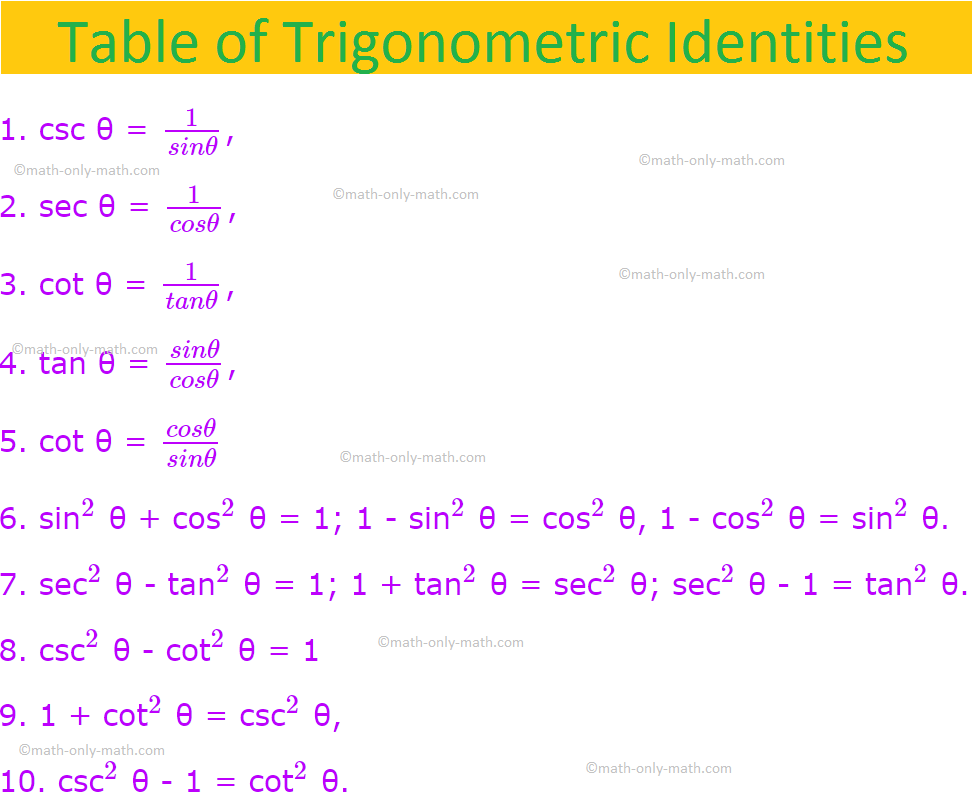
Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify Statistics Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability MidRange Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal DistributionI am curious as to how one would prove this without changing both sides of the equation In other words going straight from $$\cot^2\theta \sec^2\theta$$ to $$\tan^2\theta \csc^2\theta$$ (or viceversa) rather than editing both sides to meet up at a certain point as I have done in my proofSin 2 (x) cos 2 (x) = 1 tan 2 (x) 1 = sec 2 (x) cot 2 (x) 1 = csc 2 (x) sin(x y) = sin x cos y cos x sin y cos(x y) = cos x cosy sin x sin y
Ilectureonline
Trig identities tan^2 theta
Trig identities tan^2 theta-We also explain what trig identities are and how you can verify trig identities In math, an "identity" is an equation that is always true, every single time Trig identities are trigonometry equations that are always true, and they're often used to solve trigonometry and geometry problems and understand various mathematical propertiesAll the trigonometric identities on one page Color coded Mobile friendly With PDF and JPG downloads Trig Identities Download PDF Download JPG Reciprocal Identities I highly recommend this 3minute $$ \tan(2\theta) = \frac{2\tan\theta}{1\tan^2\theta} $$



2sinxcosx Identity Gamers Smart
Nov 09, · Sine, tangent, cotangent and cosecant in mathematics an identity is an equation that is always true Meanwhile trigonometric identities are equations that involve trigonometric functions that are always true This identities mostly refer to one angle labelled $ \displaystyle \thetaWhen working with trigonometric identities, it may be useful to keep the following tips in mind Draw a picture illustrating the problem if it involves only the basic trigonometric functions If the problem expresses an identity between trigonometric functions, try working on one side of the identity to write the trigonometric functions from one side in terms of trigonometric functionsTrigonometric Identities Questions Solve the below practice questions based on the trigonometry identities that will help in understanding and applying the formulas in an effective way Express the ratios cos A, tan A and sec A in terms of sin A Prove that sec A (1 – sin A)(sec A tan A) = 1 Find the value of 7 sec 2 A – 7 tan 2 A
Mar 08, 16 · We will use the identity tanθ = 2tan(θ 2) 1 − tan2(θ 2) Let x = tan(θ 2) then tanθ = 2x 1 −x2 or tanθ(1 −x2) = 2x or −tanθx2 −2x tanθ = 0 orProve the Following Trigonometric Identities (1 Tan^2 Theta)/(1 Cot^2 Theta) = ((1 Tan Theta)/(1 Cot Theta))^2 = Tan^2 Theta CBSE CBSE (English Medium) Class 10 Question Papers 6 Textbook Solutions Important SolutionsTrigonometric Identities From Math Wiki Jump to navigation Jump to search Contents 1 List of identities;
Sep 01, · To sum up, only two of the trigonometric functions, cosine and secant, are even The other four functions are odd, verifying the evenodd identities The next set of fundamental identities is the set of reciprocal identities, which, as their name implies, relate trigonometric functions that are reciprocals of each other (Table \(\PageIndex{3}\))Using double angle identities in trigonometry Identities in math shows us equations that are always true There are many trigonometric identities (Download the Trigonometry identities chart here ), but today we will be focusing on double angle identities, which are named due to the fact that they involve trig functions of double angles such as sin θ \theta θ, cos2 θ \theta θ, and tan2Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor



Prove The Following Trigonometric Identities 1 Cot 2theta 1
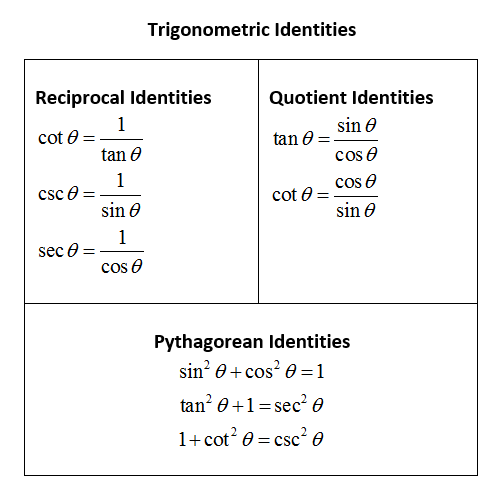


Trigonometric Identities Simplify Expressions Video Lessons Examples And Solutions
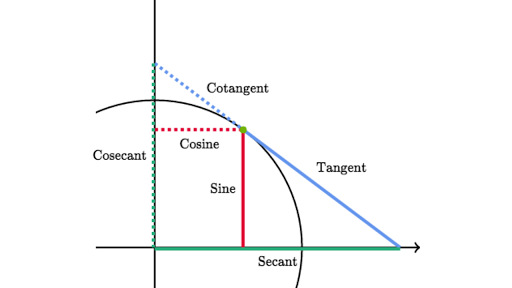
$\tan^2{\theta} \,=\, \sec^2{\theta}1$ The square of tan function equals to the subtraction of one from the square of secant function is called the tan squared formula It is also called as the square of tan function identity Introduction The tangent functions are often involved in trigonometric expressions and equations in square form TheSome Useful Trigonometric Identities An identity is an equation whose left and right sides when defined are always equal regardless of the values of the variables the two sides contain Some very useful trigonometric identities are shown belowTrigonometric functions specify the relationships between side lengths and interior angles of a right triangle For example, the sine of angle θ is defined as being the length of the opposite side divided by the length of the hypotenuse Referring to the diagram at the right, the six trigonometric functions of θ are



Solved Establish The Identity 1 Tan 2 Theta 1 Tan 2 Chegg Com



Trigonometric Identities A Plus Topper
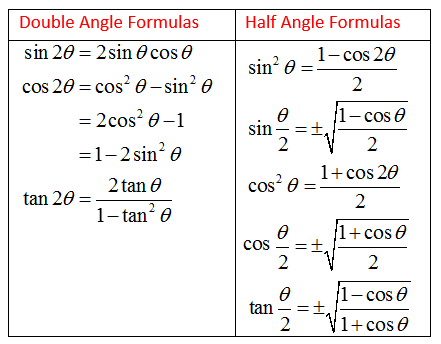
Subsection The Double Angle Identities Another useful type of trigonometric identities are the double angle identitiesThe double angle identities allow us to take trigonometric equations with \(2\theta\) and replace them with trigonometric expressions containing just \(\theta\text{}\)\(\displaystyle 3s 7s = 10s\)Mar 21, 19 · 71 Solving Trigonometric Equations with Identities For the exercises 16, find all solutions exactly that exist on the interval \(0,2\pi )\) 1) \(\csc ^2 t=3\)
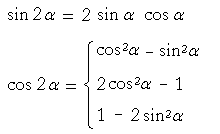


Trigonometric Identities Topics In Trigonometry



Sec 6x Tan 6x 1 2 Tan 2x Sec 2x Important Difficult Trigonometric Identity Youtube
The main trigonometric identities between trigonometric functions are proved, using mainly the geometry of the right triangle For greater and negative angles, see Trigonometric functions Elementary trigonometric identities Definitions Trigonometric functions specify the relationships between side lengths and interior angles of a rightDouble Angle Values and Trigonometric Identities The value of a cosine function is obtained when we'll divide the number {eq}1 {/eq} by the integer value of the secant function and then simplify62 Trigonometric identities (EMBHH) An identity is a mathematical statement that equates one quantity with another Trigonometric identities allow us to simplify a given expression so that it contains sine and cosine ratios only



Prove The Following Trigonometric Identities Cot 2theta 1 S



14 2 Trigonometric Identities
In an identity, the expressions on either side of the equal sign are equivalent expressions, because they have the same value for all values of the variable Identity An identity is an equation that is true for all legitimate values of the variables Example 541 Which of the following equations are identities?Visit http//ilectureonlinecom for more math and science lectures!In this video I will solve tan^2(theta)4=0, theta=?RD Sharma solutions for Class 10 Maths chapter 11 (Trigonometric Identities) include all questions with solution and detail explanation This will clear students doubts about any question and improve application skills while preparing for board exams The detailed, stepbystep solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clear your confusions, if any



Half Angle Calculator



14 2 Trigonometric Identities
Feb 03, 18 · This is just a list of formulas that I've found to be the most useful in a Calculus class For a complete listing of trig formulas you can download my Trig Cheat Sheet Complete the following formulas Show All Solutions Hide All Solutions \({\sin ^2}\left( \theta \right) {\cos ^2}\left( \theta \right) = \) Show SolutionProve trigonometric identity for $\tan^2(\theta/2)$ Ask Question Asked 7 years, 3 months ago Active 4 years, 9 months ago Viewed 160 times 0 $\begingroup$ I've been at this for a couple of days (34 hours total now), and am feeling lost $$(1)\ \tan^2(\frac{1}{2}\theta) = \frac{\tan(\theta) \sin(\theta)}{\tan(\theta)\sin(\theta)}$$Basic Trig Identities The basic trig identities or fundamental trigonometric identities are actually those trigonometric functions which are true each time for variablesSo, these trig identities portray certain functions of at least one angle (it could be more angles) It is identified with a unit circle where the connection between the lines and angles in a Cartesian plane



11 Basic Trigonometric Identities An Identity Is An Equation That Is True For All Defined Values Of A Variable We Are Going To Use The Identities To Ppt Download


Prove That Math Tan 2 Theta 1 Sec 2 Theta Math Quora
Subsection Trigonometric Identities A trigonometric identity is a trigonometric equation that is true for every possible value of the input variable on which it is defined Identities are usually something that can be derived from definitions and relationships we already knowFollowing table gives the double angle identities which can be used while solving the equations You can also have #sin 2theta, cos 2theta# expressed in terms of #tan theta # as under #sin 2theta = (2tan theta) / (1 tan^2 theta)# #cos 2theta = (1 tan^2 theta) / (1 tan^2 theta)#Look up AND understand all your favorite trig identities Google Classroom Facebook Twitter Email Using trigonometric identities Finding trig values using angle addition identities Practice Find trig values using angle addition identities Using trig angle addition identities
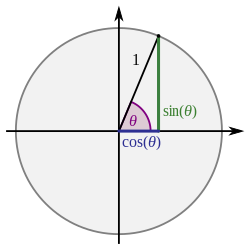


List Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia


What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora
Trig substitution assumes that you are familiar with standard trigonometric identies, the use of differential notation, integration using usubstitution, and the integration of trigonometric functions Recall that if $$ x = f(\theta) \ , $$ $$ dx = f'(\theta) \ d\theta $$ For example, if $$ x = \sec \theta \ , $$ then $$ dx = \sec \theta \tanList of identities Given two functions f and g, we say f = g if f(x) = g(x) for all every x in the domain of both f and gFree math lessons and math homework help from basic math to algebra, geometry and beyond Students, teachers, parents, and everyone can find solutions to their math problems instantly
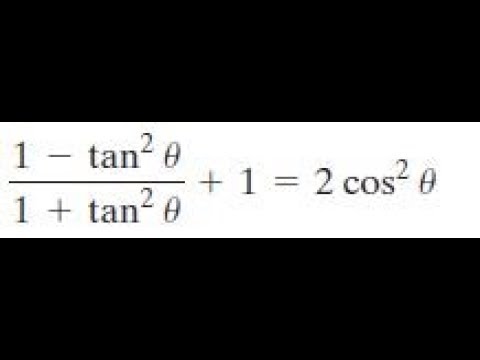


1 Tan 2x 1 Tan 2 X 1 2cos 2 X Youtube
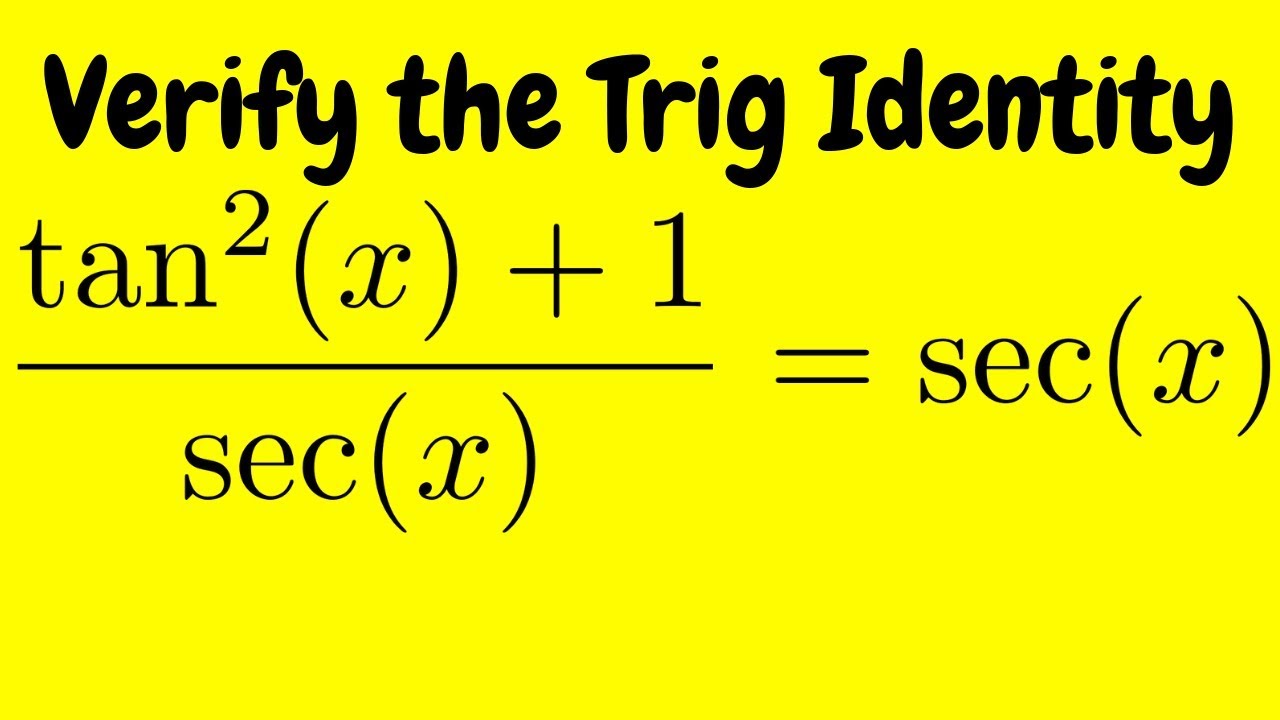


Verifying A Trigonometric Identity Tan 2 X 1 Sec X Sec X Youtube
Mar 03, 19 · Trigonometry is one of the important branches of Mathematics It is the study of triangles and its measurement In this article, we come across the trigonometric ratios, graphs of trigonometric functions, identities, maximum and minimumMar 05, 18 · Evaluate \( \displaystyle \int{{{{\sec }^6}\left( {3y} \right){{\tan }^2}\left( {3y} \right)\,dy}}\) Show All Steps Hide All Steps Hint Pay attention to the exponents and recall that for most of these kinds of problems you'll need to use trig identities to put the integral into a form that allows you to do the integral (usually with a CalcWhat are the relations among all the trigonometrical ratios of (180° θ)?
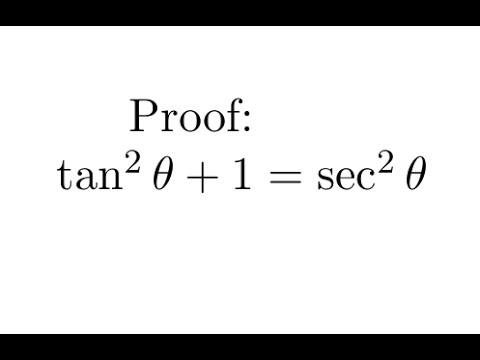


Proof Tan 2 1 Sec 2 Youtube
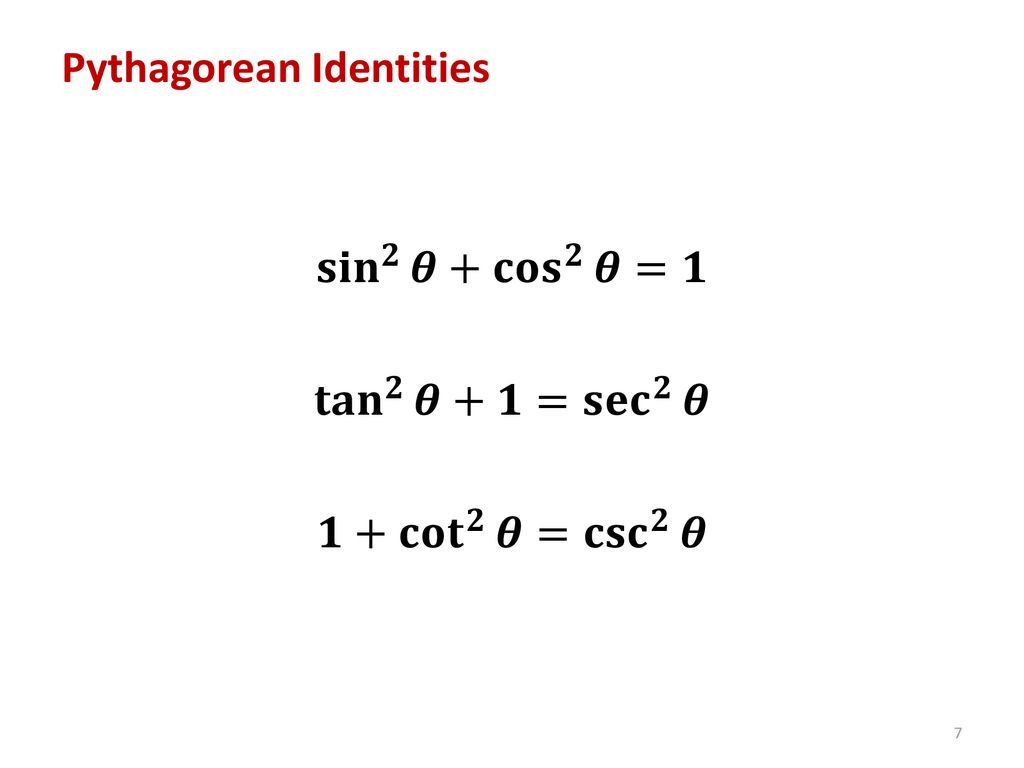


5 1 5 2 Trigonometric Identities Ppt Download
The particular algebraic properties of the trigonometric functions, mainly the Pythagorean identities, $$ \begin{align} sin^2(\theta) cos^2(\theta) &= 1 \\5pt tan^2(\theta) 1 &= sec^2(\theta) \\5pt cot^2(\theta) 1 &= csc^2(\theta) \end{align}$$ will give us the hook we need to solve some otherwise very tricky integralsAnswer to Given tan \theta = 2, use trigonometric identities to find the exact value of each of the following (a) sec^2\theta (b) cot \theta, (c)Aug 08, 13 · let's do some examples simplifying trigonometric expressions so let's say that I have 1 minus sine squared theta and this whole thing times cosine cosine squared theta so how could I simplify this well the one thing that we do know this is the most fundamental trig identity this comes straight out of the unit circle is that cosine squared theta plus sine squared theta is



Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia


Much From Little
This question has me stuck Use the Pythagorean identity sin^2 Θ cos^2 Θ = 1 to derive the other Pythagorean identities, 1 tan^2 Θ = sec^2 Θ and 1 cot^2 Θ = csc^2 Θ Discuss how to remember these identities and other You can view more similar questions or ask a new questionFree trigonometric identity calculator verify trigonometric identities stepbystep This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience ByIn trigonometrical ratios of angles (180° θ) we will find the relation between all six trigonometrical ratios


The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl


Trigonometric Identities List Of Trigonometric Identities Examples


Solving Trigonometric Equations With Identities Precalculus Ii


Trig Identity Reference Article Khan Academy



Solved Use The Trigonometric Identities To Simplify The E Chegg Com



Summary Of Trigonometric Identities
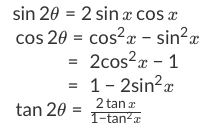


How To Use Double Angle Identities Studypug



Solved Prove The Following Identities Tan 2theta 2 Tan Chegg Com


Complex And Trigonometric Identities Introduction To Digital Filters
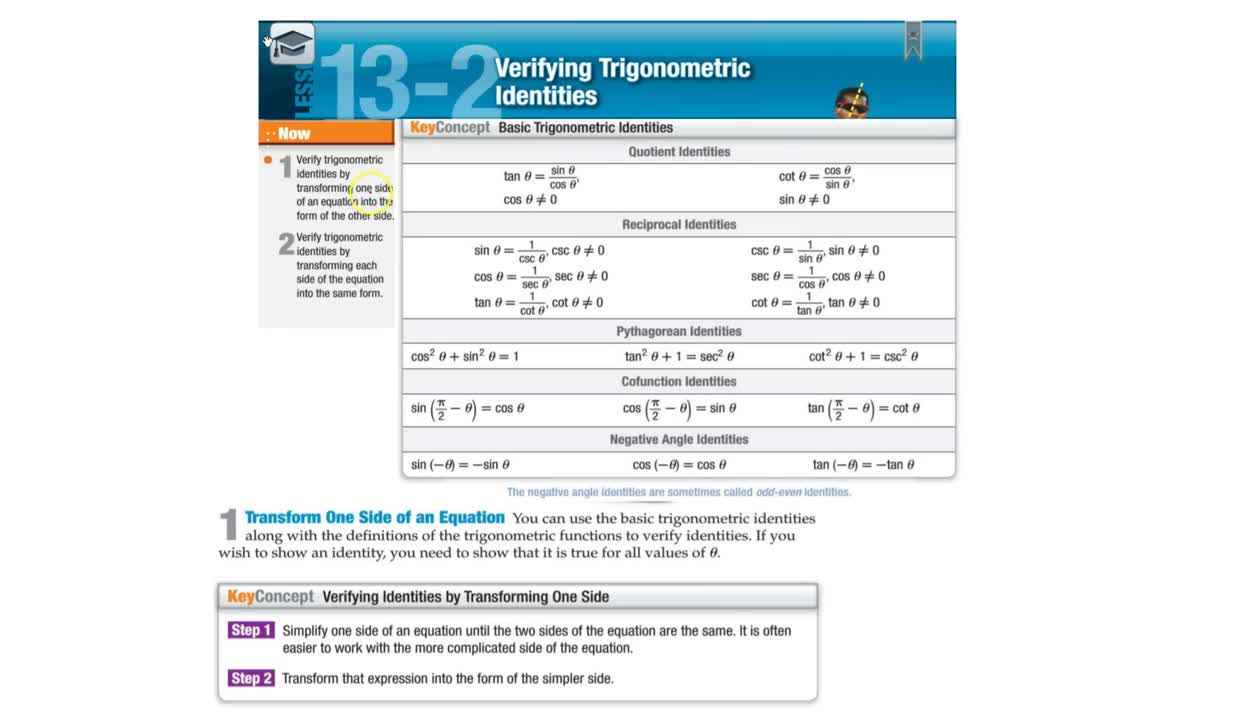


Honors Algebra 2 Trig Notes Chapter 13 Section 2 Bishop Amat Memorial High School
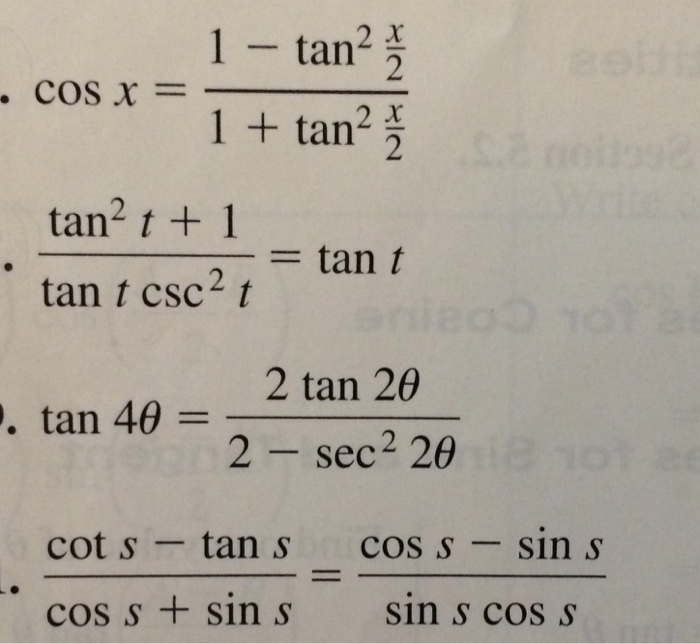


Solved Cos X 1 Tan 2 X 2 1 Tan 2 X 2 Tan 2 T 1 Ta Chegg Com



5 1 Fundamental Trig Identities Sin 1cos 1tan 1 Csc Sec Cot Csc 1sec 1cot 1 Sin Cos Ppt Download
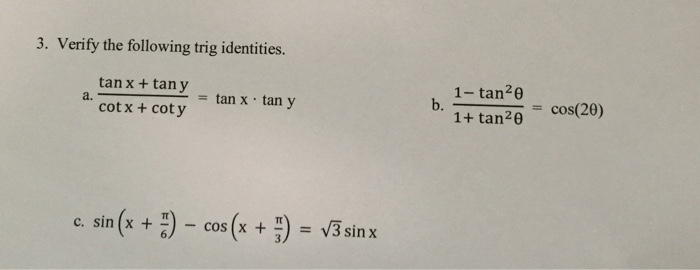


Solved Verify The Following Trig Identities A Tan X T Chegg Com



The Reciprocal Trigonometric Functions Problem 3 Trigonometry Video By Brightstorm
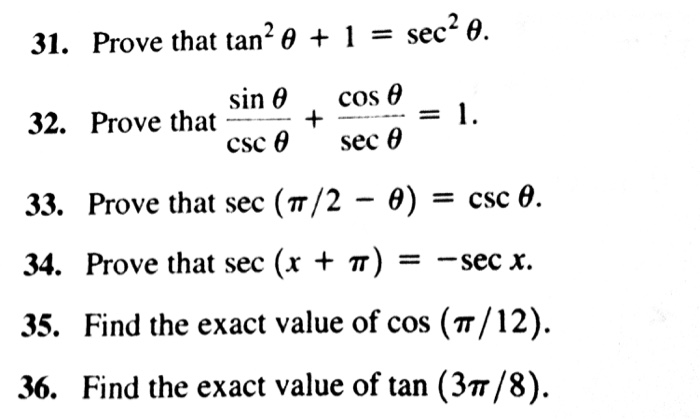


Solved 31 Prove That Tan 2 Theta 1 Sec 2 Theta 32 Chegg Com



Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像


Ilectureonline
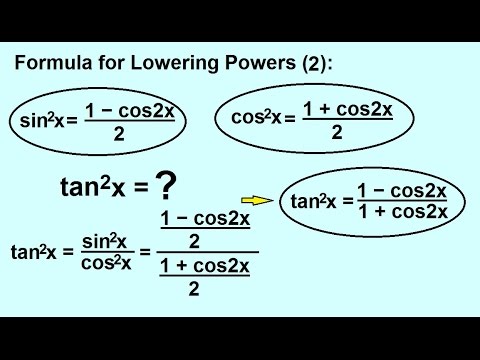


Precalculus Trigonometry Trig Identities 29 Of 57 Formula For Lowering Power Tan 2 X Youtube


Ilectureonline


Derivatives Of Trigonometric Functions
x-1=sec(squared)x.jpg)


10 Identity Tan Squared X 1 Sec Squared X Trigonometry Educator Com
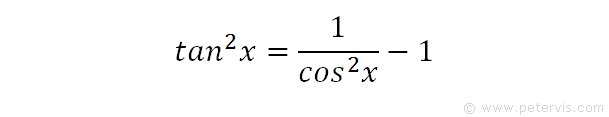


Integrate Tan 2x


Summary Of Trigonometric Identities
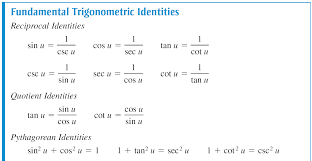


How Do You Use The Fundamental Trigonometric Identities To Determine The Simplified Form Of The Expression Socratic



List Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia


Prove That Math Tan 2 Theta 1 Sec 2 Theta Math Quora
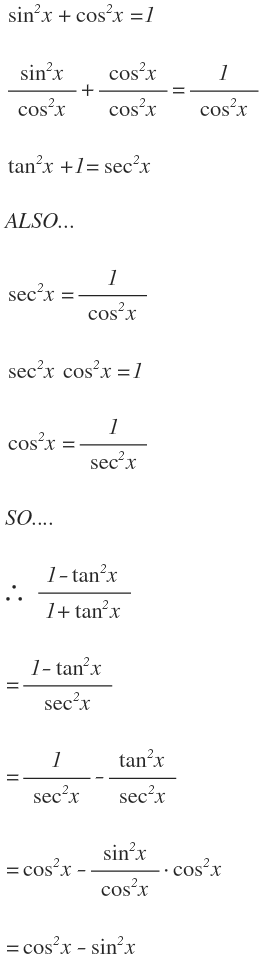


How Do You Simplify 1 Tan 2 X 1 Tan 2 X Socratic
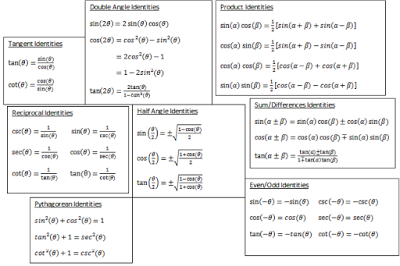


How Do You Verify The Identity Tan2theta 2 Cottheta Tantheta Socratic



Summary Of Trigonometric Identities
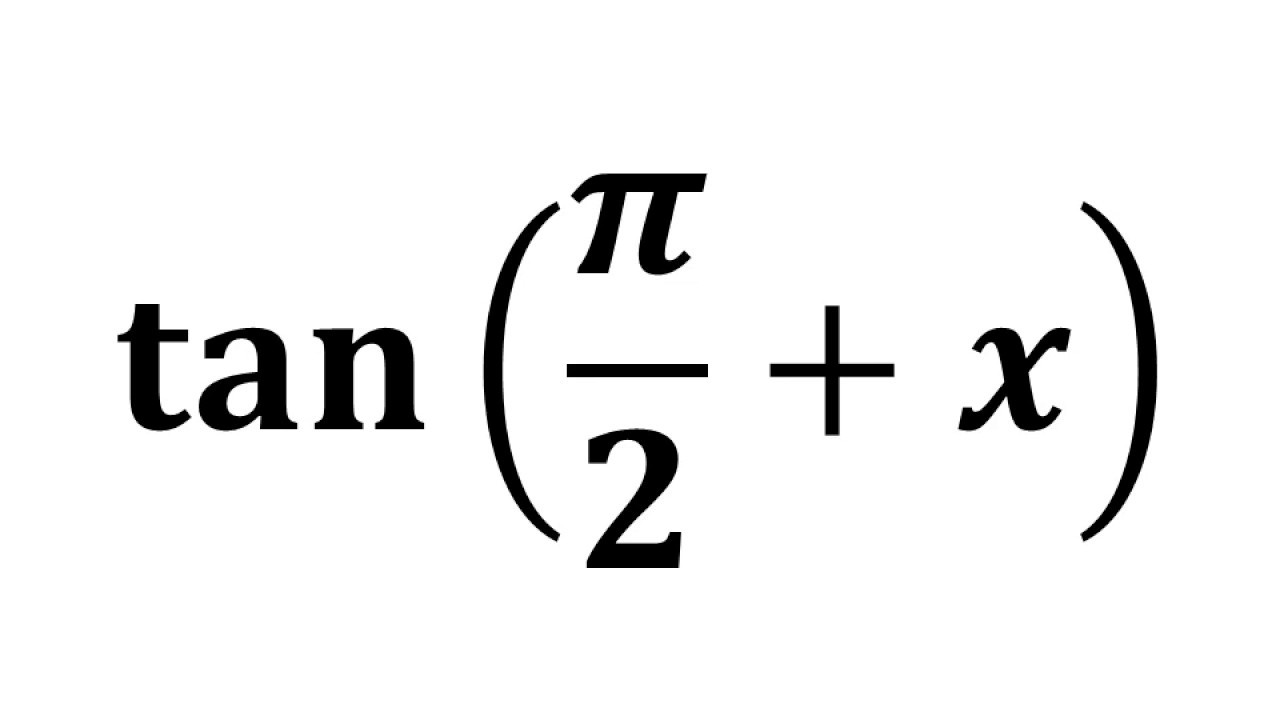


Tan Pi 2 X Tan Pi 2 Theta Youtube



2sinxcosx Identity Gamers Smart


Trigonometry Reciprocal Identities Expii



1 Tan 2x 1 Cos 2x Sin 2x 2sin 4x 1 Sin 2x Trigonometric Identities Mcr3u Youtube


How To Solve Tan 2xsin 2x Tan 2x Sin 2x Trigonometry Trigonometric Identities Youtube


Trigonometry Identities
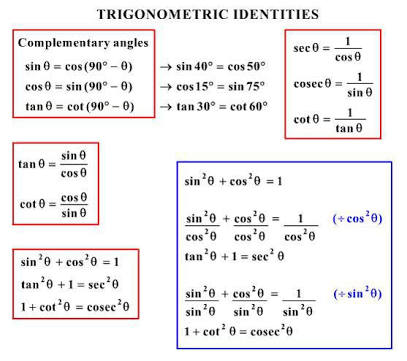


How Do You Simplify The Expression Sin 2theta Cos 2theta Cos 2theta Socratic
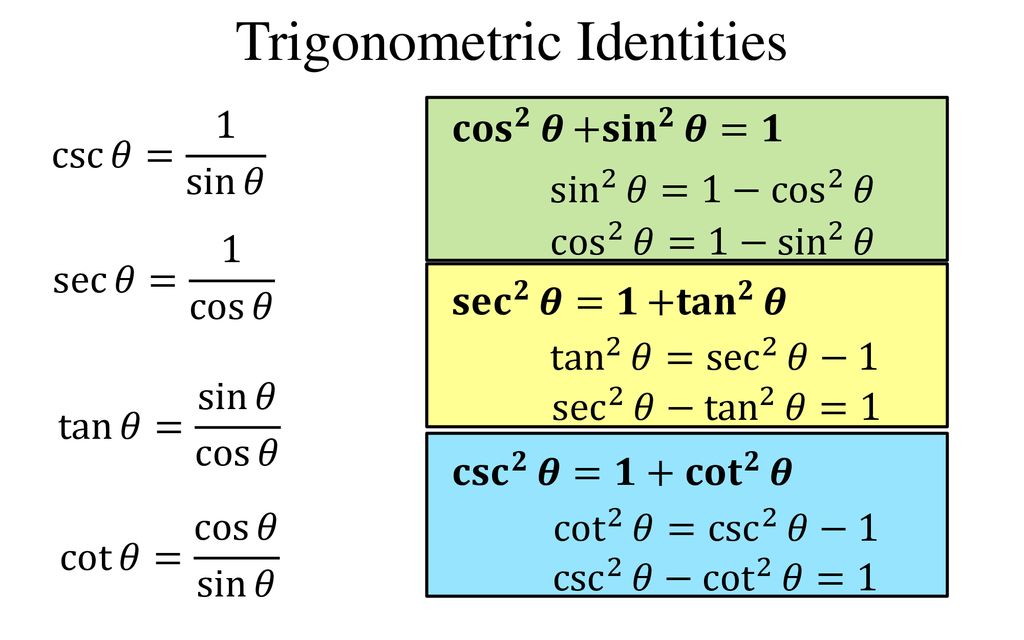


Trigonometric Identities And Equations Ppt Download
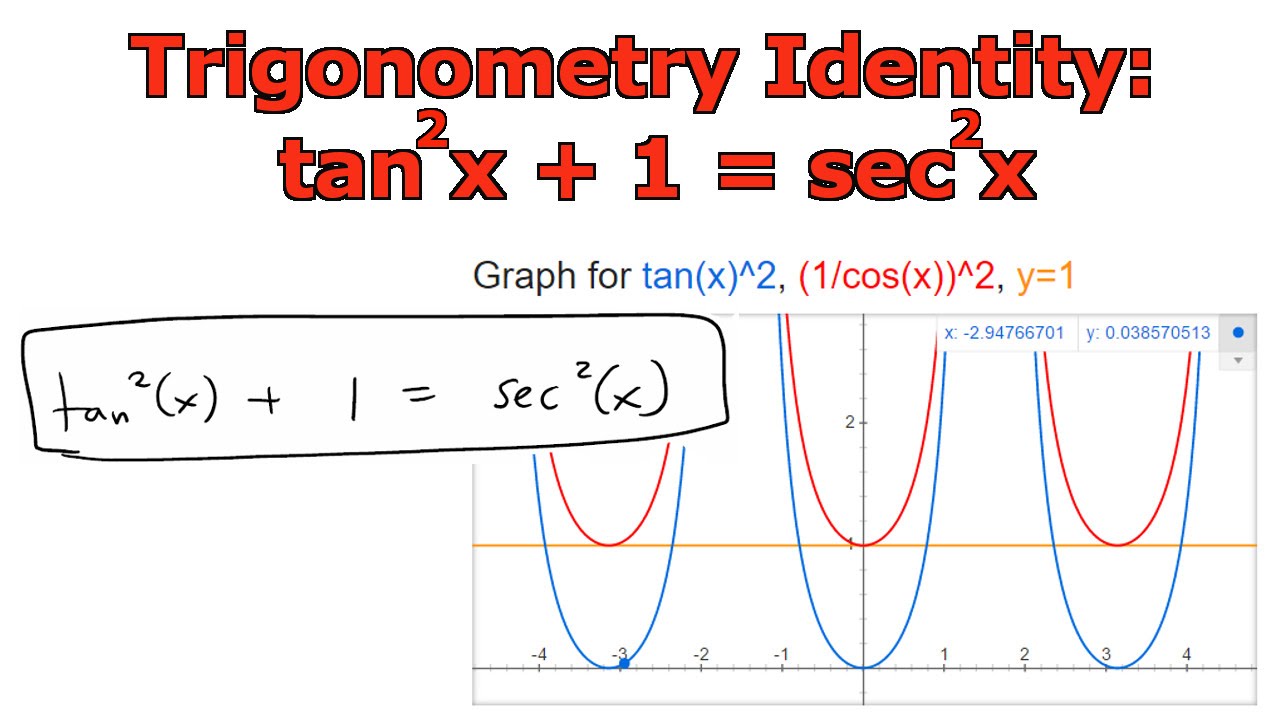


Trigonometry Identity Tan 2 X 1 Sec 2 X Youtube


Cochranmath Solving Trigonometric Equations
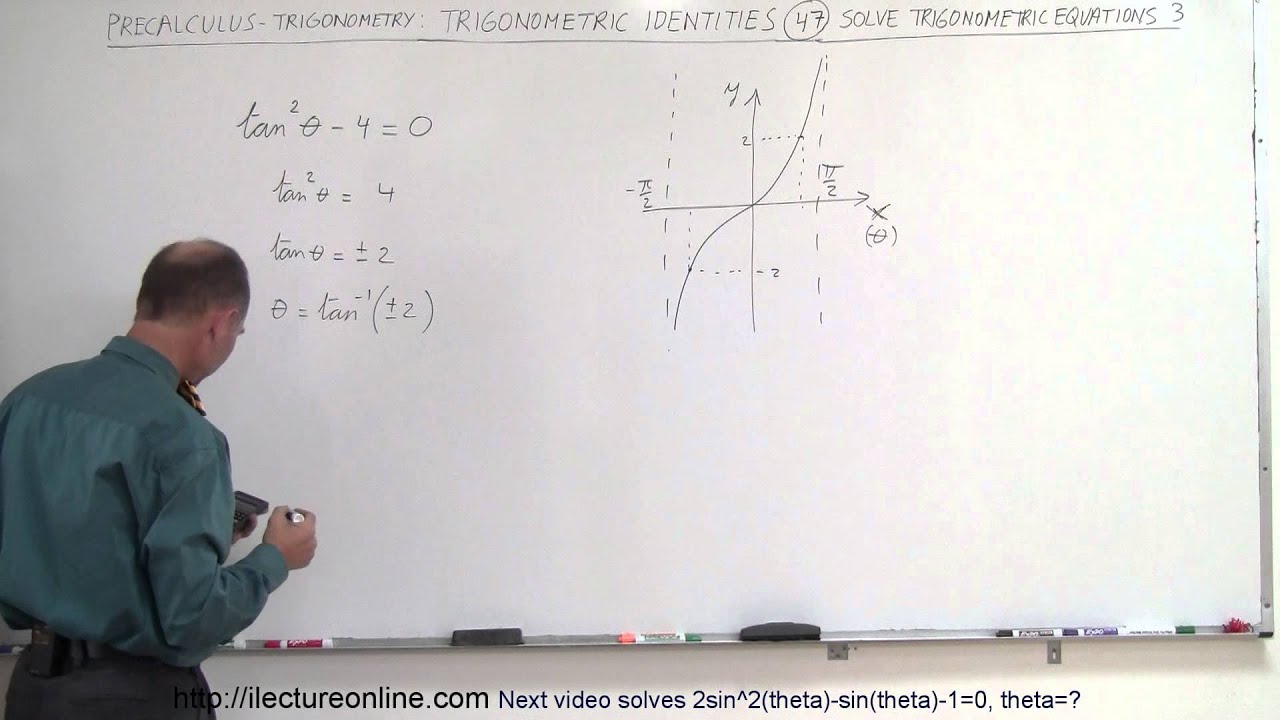


Precalculus Trigonometry Trig Identities 47 Of 57 Solve Tan 2 Theta 4 0 Theta Youtube


How Do You Verify Tan 28 Sin 28 Tan 28sin 28 Socratic
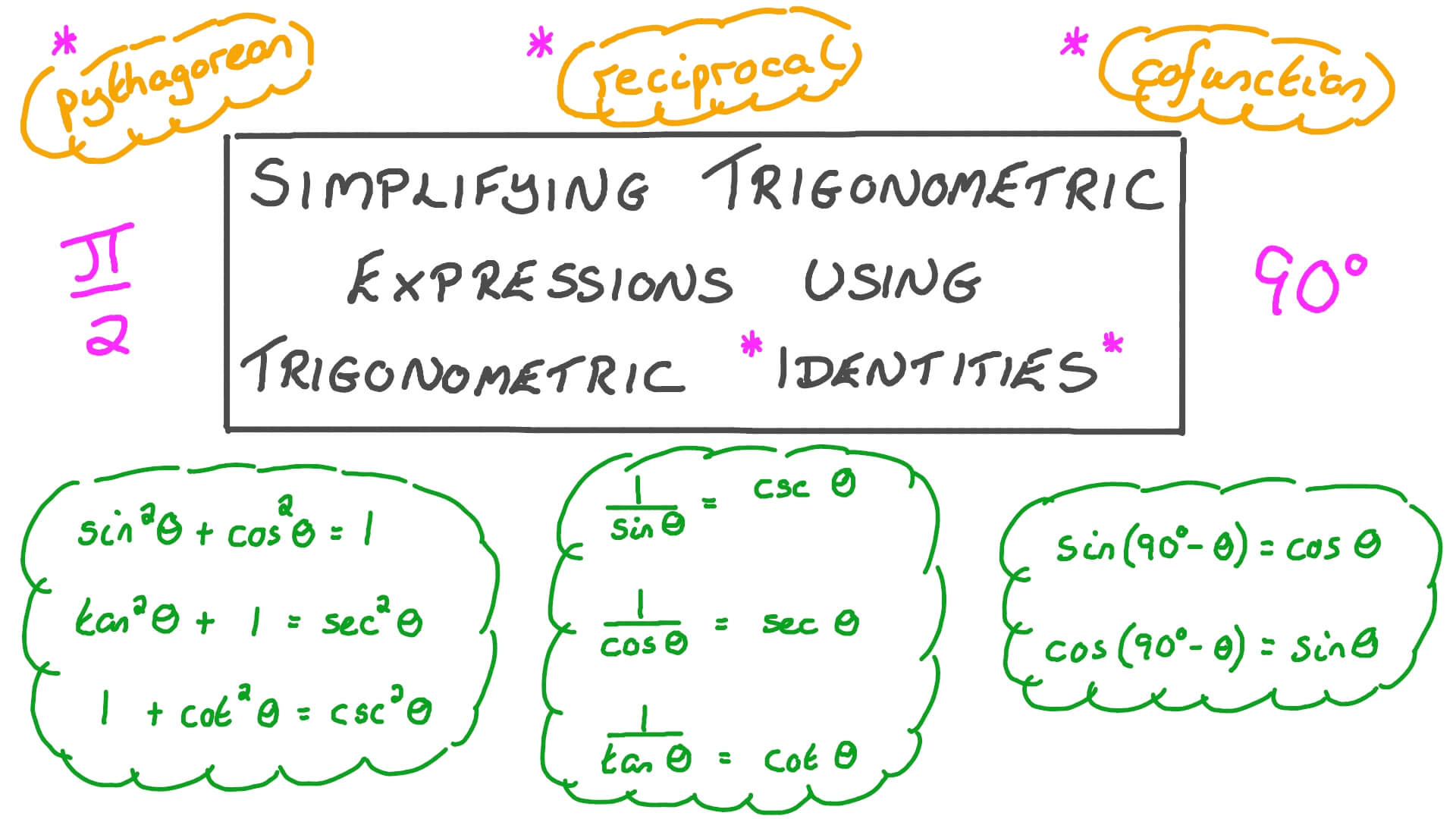


Lesson Video Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions Using Trigonometric Identities Nagwa
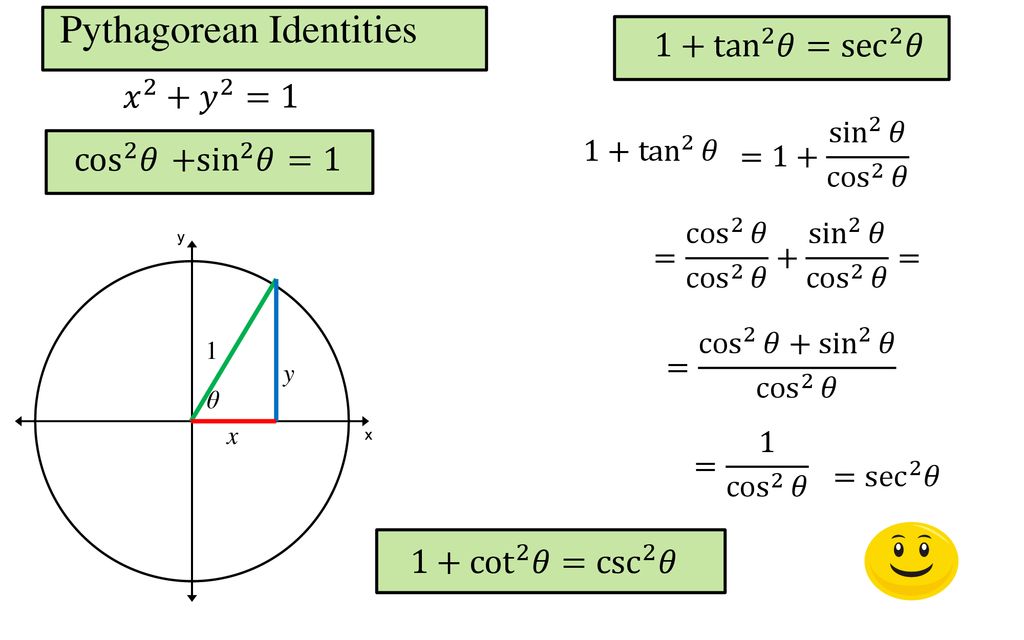


Trigonometric Identities And Equations Ppt Download



Warm Up Prove Sin 2 X Cos 2 X 1 This Is One Of 3 Pythagorean Identities That We Will Be Using In Ch 11 The Other 2 Are 1 Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Ppt Download
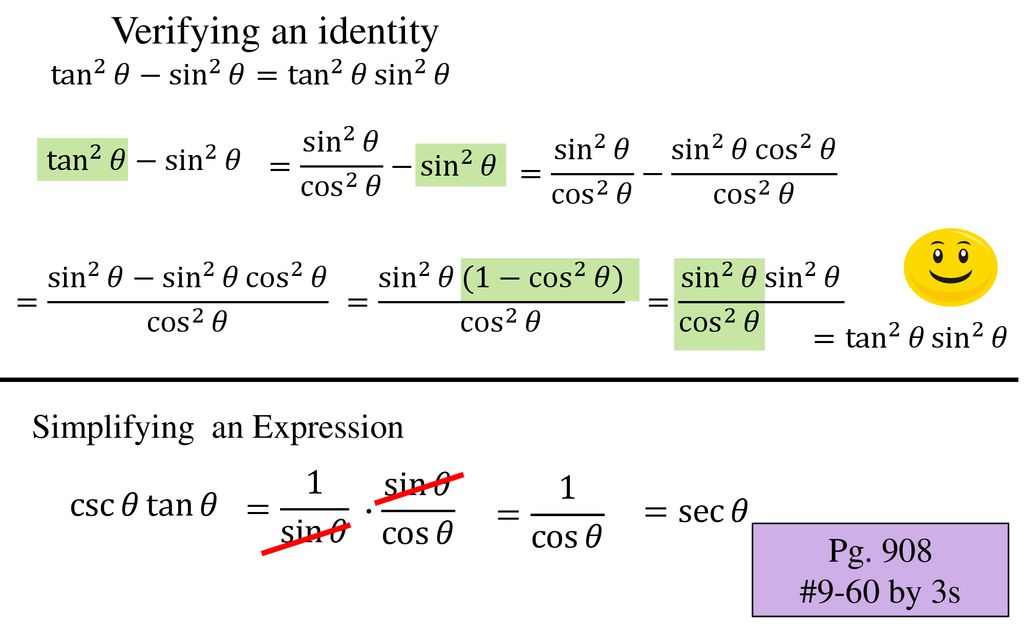


Trigonometric Identities And Equations Ppt Download


Solving Trigonometric Equations With Identities Precalculus


What Are The Quotient Identities For A Trigonometric Functions Socratic


How I Remember Trig Identities Part 2 Beyond Solutions
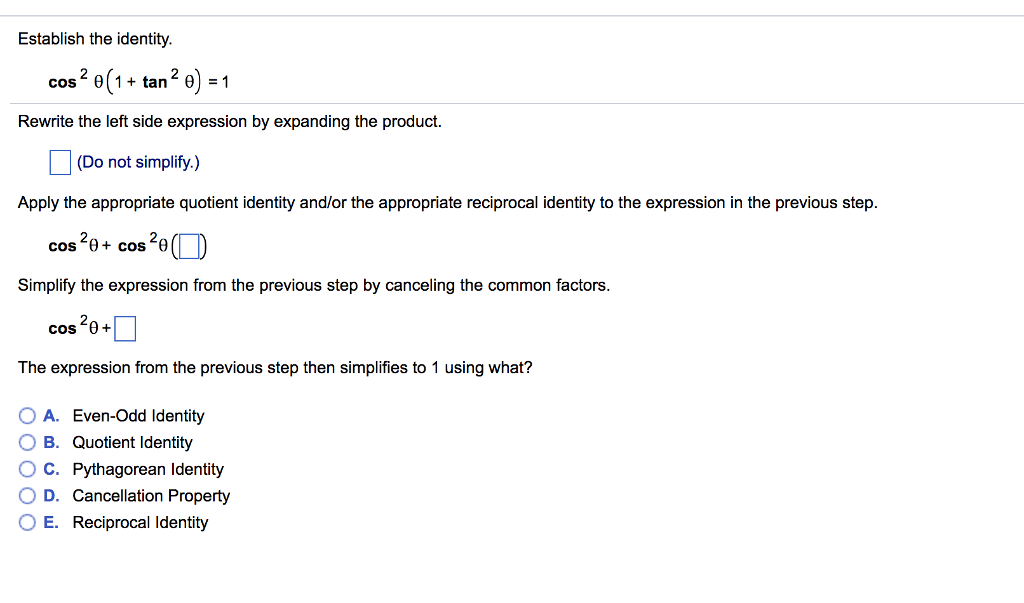


Solved Establish The Identity Cos 2 8 1 Tan 2 8 1 Rew Chegg Com



Solved Find All Solutions Of The Following Equations Betw Chegg Com
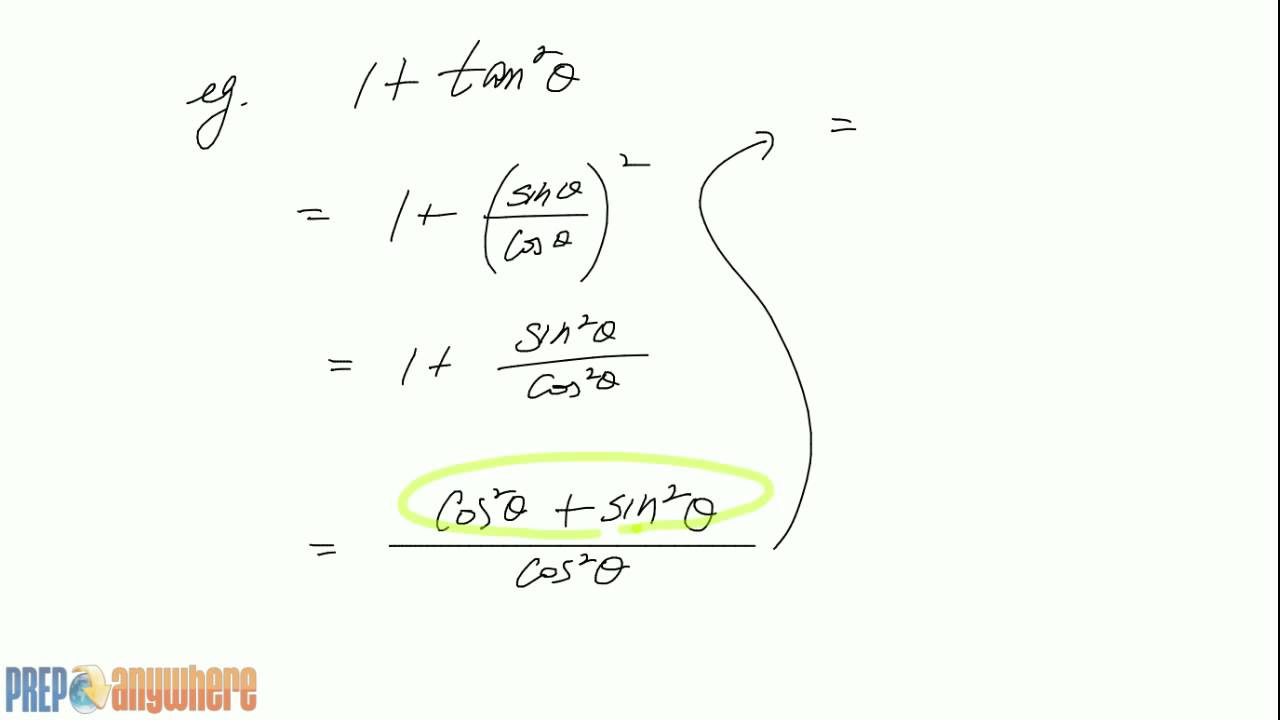


3 Simplifying Trig Expression 1 Tan 2x Youtube



Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 6 Trigonometric Identities Exercise 6 1 Get Pdf
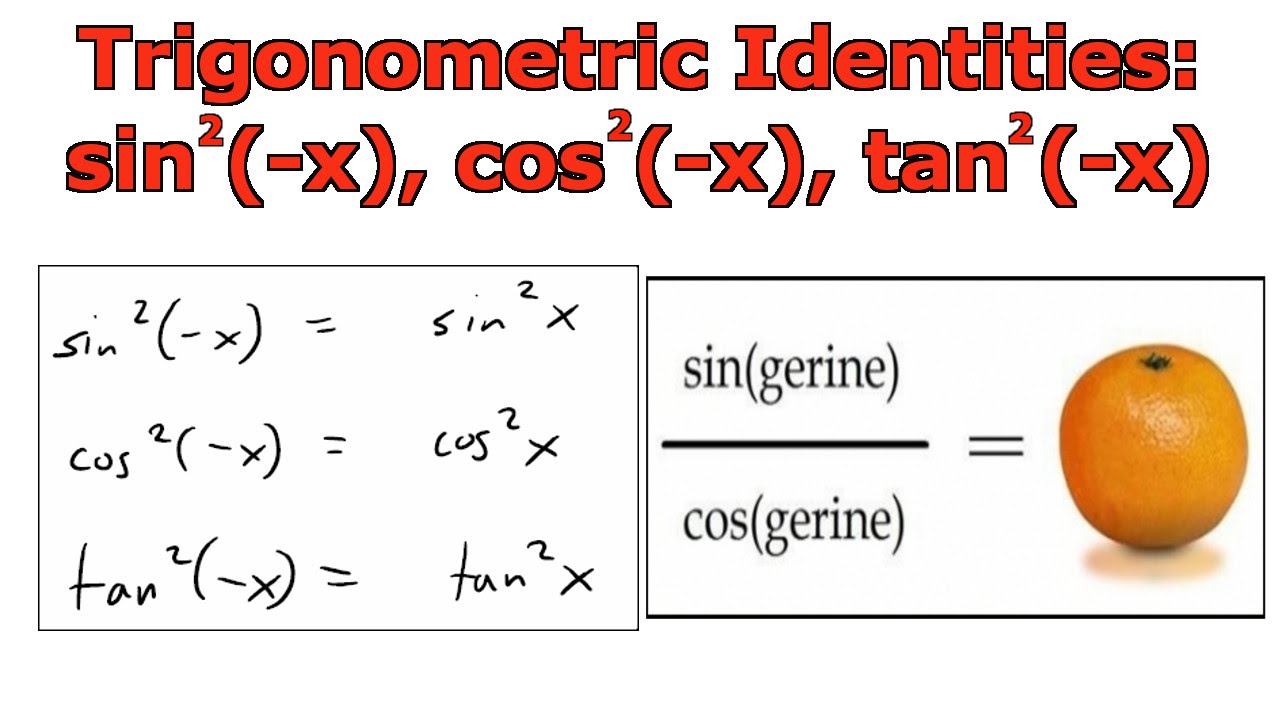


Trigonometric Identities Sin 2 X Cos 2 X Tan 2 X Youtube


Ilectureonline



What Is The Value Of Sin 2theta 1 1 Tan 2theta



Solved 1 Given The Triangle Below Calculate The Followi Chegg Com



Integrate Cosec 2x



Solved Verify Prove The Following Trigonometric Identit Chegg Com


Trig Identities Crossword Wordmint



Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia
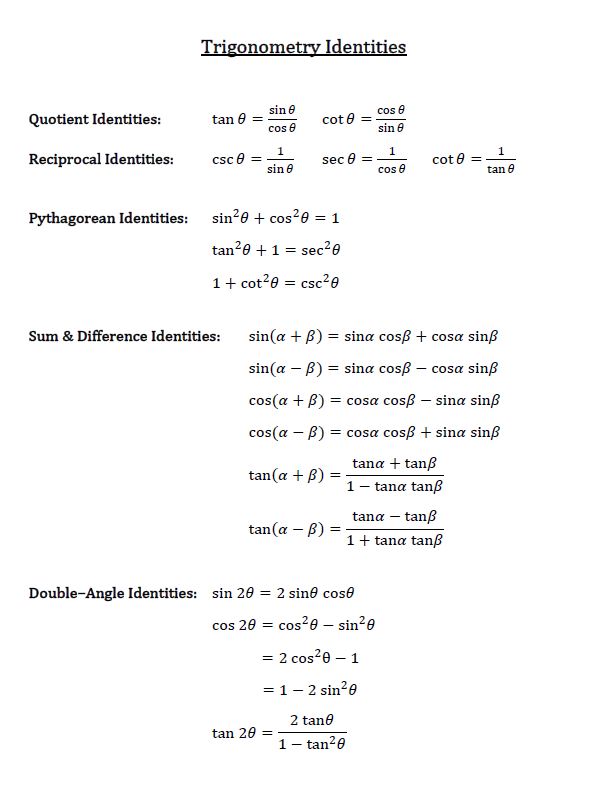


How To Use Double Angle Identities Studypug



Warm Up Prove Sin 2 X Cos 2 X 1 This Is One Of 3 Pythagorean Identities That We Will Be Using In Ch 11 The Other 2 Are 1 Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Ppt Download



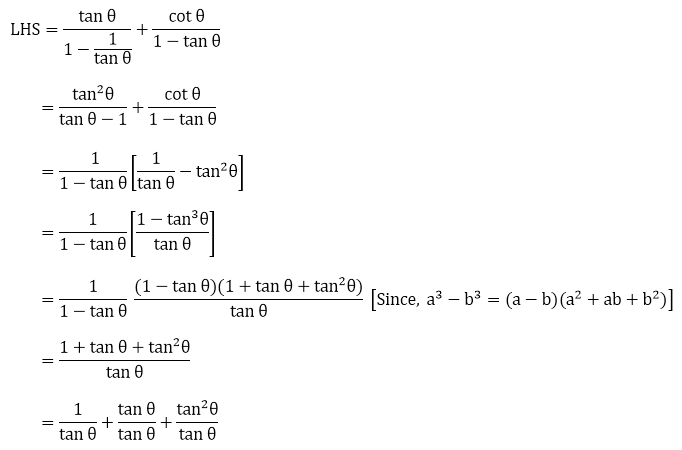
Solved Establish The Identity Tan 12 Theta 3 Tan 4 Chegg Com



Trigonometric Identities A Plus Topper



Art Of Problem Solving
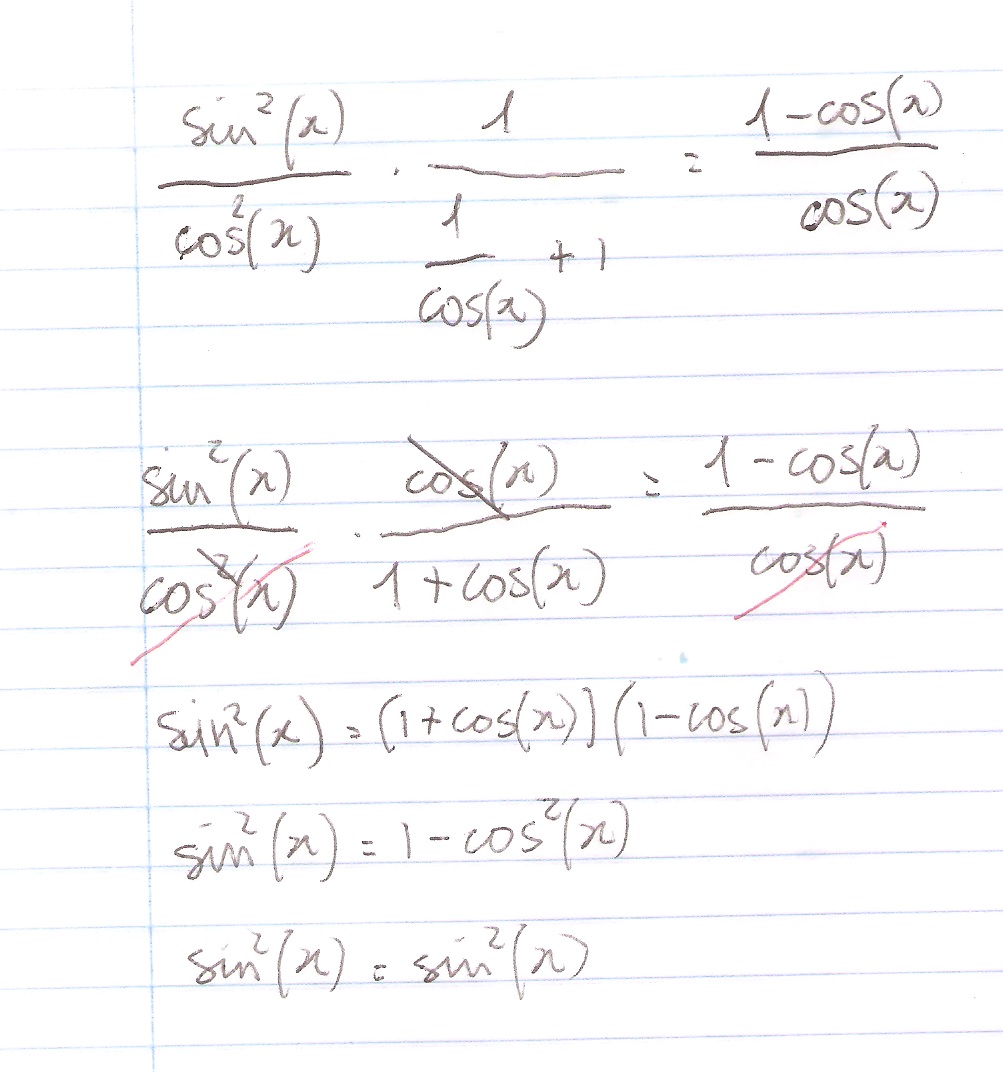


How Do You Prove The Identity Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Cosx Cosx Socratic


Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 6 Trigonometric Identities Exercise 6 1 Get Pdf


What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora
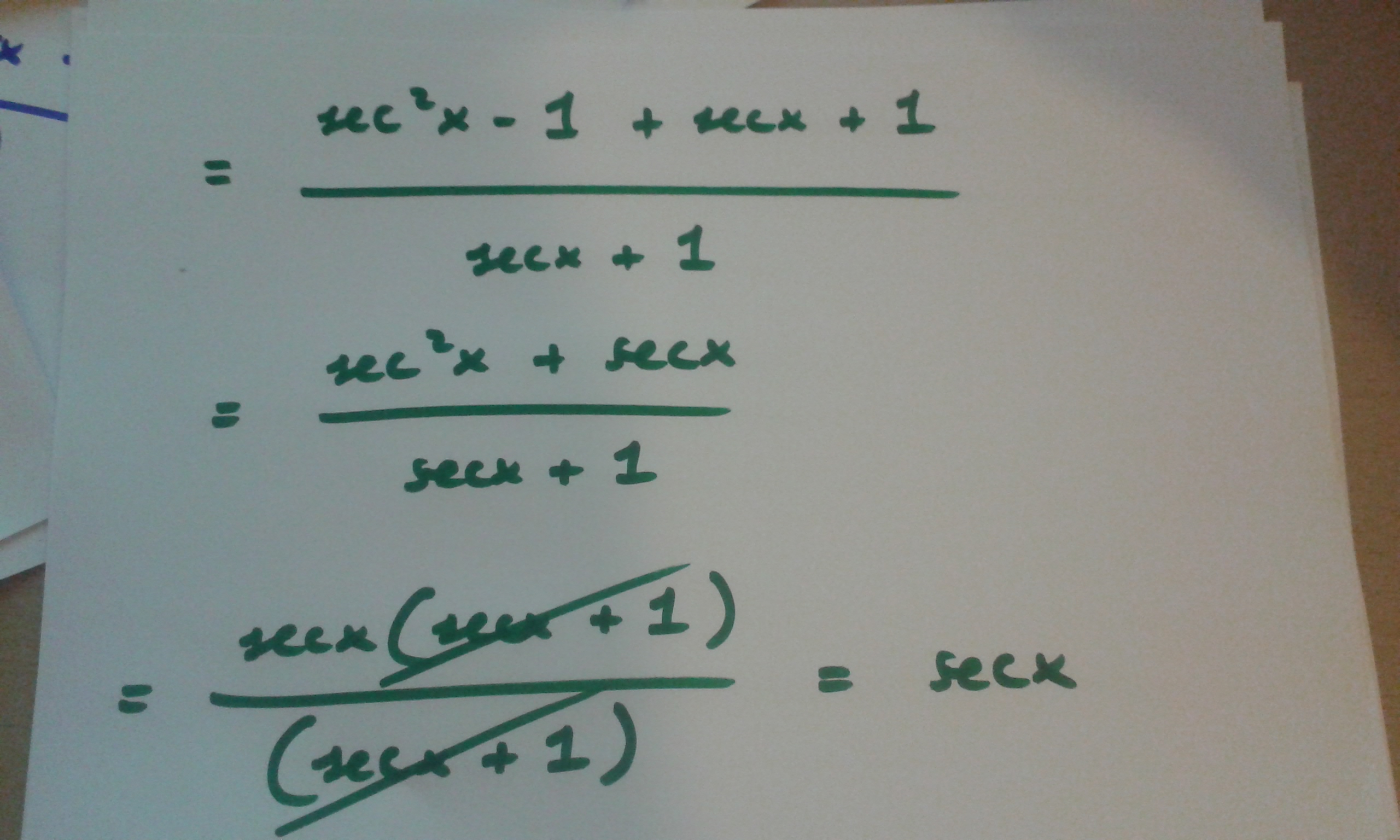


How Do You Prove Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Secx Socratic



How Does The Trigonometric Identity 1 Cot 2 Theta Csc 2 Theta Derive From The Identity Sin 2 Theta Cos 2 Theta 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Trigonometric Identities
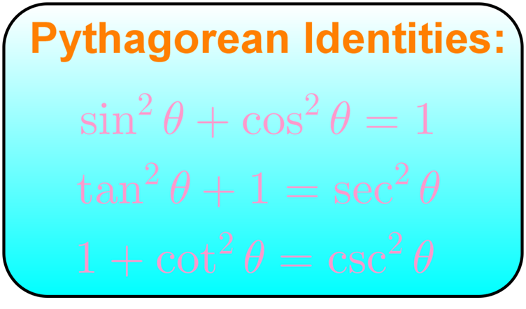


Understanding Pythagorean Identities Studypug
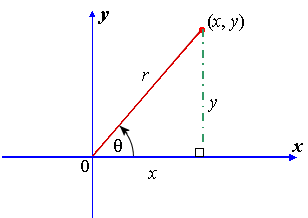


1 Trigonometric Identities
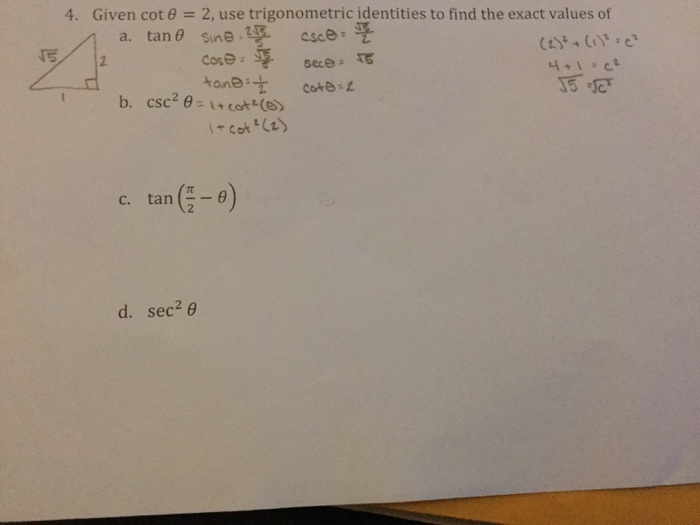


Solved Given Cot Theta 2 Use Trigonometric Identities Chegg Com


Double Angle Formula And Half Angle Formula Video Lessons Examples And Solutions



Trig Identity Sec 4x Tan 4x 1 2tan 2x Youtube



Using Trigonometric Identities Video Khan Academy



Revision Trigonometry Siyavula



How Do You Simplify Sec 4x Tan 4x Sec 2x Tan 2x Socratic



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿